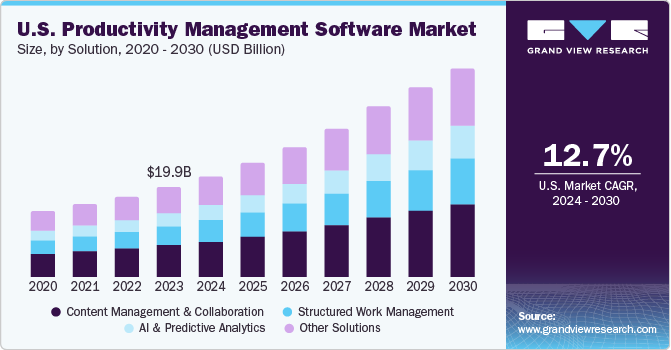
In the digital world, software plays a crucial role. Two key types are productivity software and enterprise software.
Choosing the right software can be challenging. Productivity software helps individuals manage tasks, while enterprise software supports large organizations. Understanding their differences can help in making informed decisions. This blog will explore both types, highlighting their unique features and uses.
By the end, you’ll have a clear idea of which software suits your needs. Stay with us as we dive into the comparison of productivity software versus enterprise software.
Credit: www.a3logics.com
Introduction To Software Types
Software plays a crucial role in our daily tasks. It enhances productivity and manages business operations. Understanding the types of software is essential. This blog will focus on two main types: productivity software and enterprise software.
Defining Productivity Software
Productivity software helps individuals complete tasks efficiently. Common examples include word processors, spreadsheets, and presentation tools. These tools streamline work processes. They also improve communication and collaboration. Many people use them daily.
Popular productivity software includes Microsoft Office and Google Workspace. These tools offer various features. They help users create documents, analyze data, and present information. Productivity software saves time and increases output.
What Is Enterprise Software?
Enterprise software is designed for businesses. It helps manage operations and support large-scale functions. Examples include customer relationship management (CRM) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. These tools integrate various business processes. They ensure smooth operations and better decision-making.
Enterprise software supports multiple users. It connects different departments within an organization. This software handles complex tasks and large data volumes. Companies rely on enterprise software to stay competitive.
Core Features
Understanding the core features of productivity software and enterprise software helps businesses choose the right tools. Each type of software offers unique features designed to meet specific needs. Let’s explore the key features of both to see what sets them apart.
Key Features Of Productivity Software
Productivity software aims to enhance individual efficiency. These tools include word processors, spreadsheets, and presentation software. They help users perform daily tasks quickly and easily.
Collaboration features are essential. Tools like Google Docs allow multiple users to work on a document simultaneously. This fosters teamwork and makes real-time edits possible.
Task management features keep users organized. Software like Trello helps users create task lists, set deadlines, and track progress. This ensures that projects stay on schedule.
File storage and sharing are also important. Cloud-based services like Dropbox provide secure storage. Users can access their files from anywhere, which is convenient for remote work.
Essential Features Of Enterprise Software
Enterprise software serves large organizations. These tools include customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and human resource management systems (HRMS).
Scalability is crucial. Enterprise software must handle large volumes of data and users. This ensures that the system can grow with the business.
Integration capabilities are key. Enterprise software must work with other systems within the organization. This ensures smooth data flow and unified operations.
Security features are vital. Enterprise software must protect sensitive company data. Features like encryption and access controls are essential to prevent unauthorized access.
Customization is another important feature. Businesses have unique needs, and enterprise software must adapt to those needs. This ensures that the system meets specific business requirements.
Use Cases
Understanding the specific use cases for productivity software and enterprise software is essential. This ensures you choose the right tools for your needs. Both types of software serve unique purposes and fit different organizational requirements.
When To Use Productivity Software
Productivity software is ideal for individual tasks and small teams. It helps streamline daily activities and boosts efficiency. Here are some scenarios where productivity software shines:
- Personal Task Management: Tools like Todoist or Microsoft To-Do help manage daily tasks.
- Collaborative Projects: Apps like Trello or Asana enable team collaboration on projects.
- Document Creation: Use Google Docs or Microsoft Word for creating and sharing documents.
- Communication: Platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams facilitate team communication.
Ideal Scenarios For Enterprise Software
Enterprise software is designed for large organizations. It supports complex business processes and ensures smooth operations. These are some scenarios where enterprise software is indispensable:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Systems like Salesforce manage customer interactions and data.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Solutions like SAP integrate various business processes.
- Human Resource Management: Tools like Workday handle HR tasks and employee data.
- Supply Chain Management: Software like Oracle SCM optimizes the supply chain process.
Choosing between productivity software and enterprise software depends on your specific needs. Evaluate your organizational requirements before making a decision.
Efficiency Comparison
In the world of software, efficiency is key. Productivity software and enterprise software are both vital. But how do they compare in terms of efficiency? This section delves into the specifics of measuring and comparing their efficiency. We will explore various aspects to provide a clearer picture.
Measuring Efficiency In Productivity Software
Productivity software aims to help individuals and small teams. It focuses on tasks like word processing, spreadsheets, and project management. Efficiency in productivity software is often measured by time-saving features. These features include templates, automation tools, and user-friendly interfaces.
Another key factor is ease of use. If the software is intuitive, users can complete tasks faster. Integration with other tools also boosts efficiency. For example, a word processor that syncs with cloud storage saves time. Users don’t need to switch between apps to save their work.
Efficiency Metrics In Enterprise Software
Enterprise software caters to large organizations. It handles complex tasks like resource planning, customer relationship management, and supply chain management. Efficiency in enterprise software is measured by performance metrics. These metrics include system uptime, processing speed, and data accuracy.
Scalability is another crucial factor. The software must handle increasing amounts of data without slowing down. Integration with other enterprise systems is also essential. Seamless data flow between departments boosts overall efficiency.
Customization options further enhance efficiency. Tailored solutions meet specific business needs better than generic ones. This means less time spent on adapting workflows to fit the software.
Scalability
Scalability refers to the ability of software to handle growth. As businesses expand, their software must accommodate increased workloads. This makes scalability a crucial factor. Both productivity software and enterprise software offer different scalability features. Understanding these can help you make the right choice.
Scaling With Productivity Software
Productivity software, like Microsoft Office or Google Workspace, is designed for small to medium-sized teams. These tools are flexible. You can easily add users as your team grows.
Consider these advantages:
- Easy user management
- Cost-effective for small teams
- Quick setup and deployment
For instance, with Google Workspace, you can start with a few users. As your team grows, add more users seamlessly. This flexibility is ideal for startups and small businesses.
Enterprise Software Scalability
Enterprise software, like SAP or Oracle, is built for large organizations. These systems can handle massive data and complex processes. They are designed to scale horizontally and vertically.
Key features include:
- Support for thousands of users
- Advanced data management
- Customizable modules
Enterprise software supports high scalability. For example, SAP can manage various business processes, from HR to finance. It can integrate with other systems. This makes it suitable for large corporations.
| Feature | Productivity Software | Enterprise Software |
|---|---|---|
| User Management | Simple | Complex |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Data Handling | Basic | Advanced |
| Customization | Limited | Extensive |
Choosing the right software depends on your business needs. Small teams may benefit more from productivity software. Large organizations should consider enterprise solutions.
Integration Capabilities
Integration capabilities play a crucial role in the effectiveness of both productivity software and enterprise software. The ease with which these tools can connect with other systems determines how well they can serve a business’s needs. Let’s explore how integration capabilities differ between productivity software and enterprise software.
Integration With Other Tools
Productivity software often integrates easily with other tools. These tools are designed to improve individual efficiency and team collaboration. Common integrations include:
- Email Services: Integration with Gmail or Outlook for seamless communication.
- Calendar Apps: Sync with Google Calendar or Microsoft Outlook Calendar to manage schedules.
- File Storage: Connect with cloud storage like Google Drive or Dropbox for easy file sharing.
These integrations are typically easy to set up. They do not require extensive technical knowledge. This makes productivity software user-friendly for small teams and individuals.
Enterprise Software Integration
Enterprise software, on the other hand, requires more complex integration processes. These systems are designed to handle the needs of large organizations. Integrating enterprise software often involves:
- Custom APIs: Creating custom APIs to connect with existing systems.
- Middleware Solutions: Using middleware to facilitate communication between different software.
- Data Migration: Transferring large amounts of data from legacy systems.
The integration process can be lengthy and require specialized IT support. However, once integrated, enterprise software provides a unified platform. This enhances operational efficiency across the organization.
| Aspect | Productivity Software | Enterprise Software |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Ease | Easy, user-friendly | Complex, needs IT support |
| Common Integrations | Email, Calendar, Cloud Storage | Custom APIs, Middleware |
| Scalability | Limited | High |
Understanding these integration differences helps businesses choose the right software. It ensures smooth operations and boosts overall productivity.
Cost Considerations
Choosing productivity software often costs less than enterprise software. Larger organizations might need enterprise solutions for broader capabilities and integration, despite higher expenses.
Understanding the cost implications of software is crucial for businesses. Both productivity software and enterprise software come with distinct costs. Making the right choice depends on your business needs and budget.Cost Of Implementing Productivity Software
Productivity software often costs less upfront. Subscriptions usually range from a few dollars to hundreds per month. Some popular examples include Microsoft Office 365 and Google Workspace. These tools are designed to boost individual or team productivity. Many providers offer different plans. This allows businesses to choose based on their needs. Free trials are common. This lets you test the software before committing. Implementation is usually quick. It requires minimal IT support. Training costs are lower. Most employees are already familiar with these tools. Updates and maintenance are handled by the provider. This saves on long-term costs.Budgeting For Enterprise Software
Enterprise software can be more expensive. These solutions are designed for larger organizations. Examples include SAP and Oracle. Costs can run into thousands of dollars. Budgeting for enterprise software involves several components. Licenses, implementation, and customization are key factors. You may need to hire specialists. This adds to the overall cost. Training can be extensive. Employees need to learn new systems. This can take time and resources. Maintenance and updates are often your responsibility. This adds to ongoing costs. However, these systems offer robust features. They can handle complex business processes. This can justify the higher investment. “`User Experience
User experience plays a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of software. Whether it’s productivity software or enterprise software, how users interact with the interface impacts their overall efficiency. A user-friendly design helps users navigate the software effortlessly, making tasks more manageable. Poor user experience, on the other hand, can lead to frustration and decreased productivity. Let’s explore the user experience in both productivity software and enterprise software.
User-friendly Productivity Software
Productivity software aims to make everyday tasks easier. It often features intuitive designs and simple interfaces. Users can quickly learn how to use the tools. The software often includes tutorials and help guides to assist users. Icons and buttons are clearly labeled. This makes it easy to find features. The goal is to enhance productivity without confusion. Popular examples include word processors, spreadsheets, and project management tools. These tools are designed for individual use. They prioritize ease of use and quick access to features.
Enterprise Software User Experience
Enterprise software is more complex. It serves large organizations with various needs. The user interface can be more challenging to navigate. Enterprise software includes many features and settings. This can overwhelm new users. Training is often required to use the software effectively. Despite its complexity, enterprise software aims to streamline business processes. It integrates different functions like HR, finance, and supply chain. The goal is to improve overall efficiency. However, the initial learning curve can be steep. User experience improvements are essential for better adoption.
Security And Compliance
Security and compliance are critical factors in the digital landscape. While both productivity software and enterprise software aim to enhance efficiency, they differ in their security measures and compliance requirements. This section explores these differences.
Security In Productivity Tools
Productivity tools often prioritize user convenience. They enable quick access to features and data. However, this focus can sometimes compromise security.
Key aspects of security in productivity tools include:
- Data Encryption: Ensures that sensitive information is protected during transmission.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adds an extra layer of security beyond just passwords.
- Regular Updates: Patches vulnerabilities to protect against threats.
Despite these measures, productivity tools can be vulnerable to cyber-attacks due to their accessibility.
Compliance In Enterprise Solutions
Enterprise solutions handle large volumes of data and often operate in regulated industries. Hence, they must adhere to strict compliance standards.
Compliance in enterprise solutions involves:
| Compliance Standard | Explanation |
|---|---|
| GDPR | Protects personal data of EU citizens. |
| HIPAA | Ensures the protection of health information. |
| SOC 2 | Focuses on managing customer data based on five criteria: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. |
Enterprise solutions also implement robust access controls and audit trails to maintain compliance and security.
These measures are essential for preventing data breaches and ensuring legal adherence.

Credit: www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com
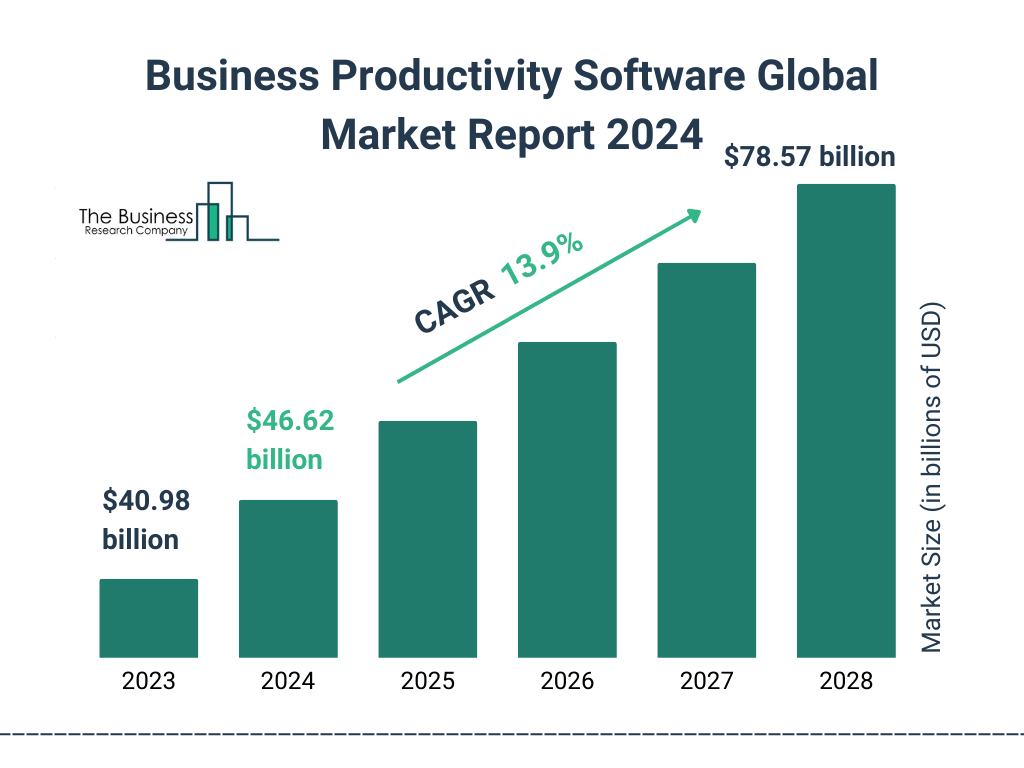
Credit: www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Productivity Software?
Productivity software helps individuals manage tasks efficiently. It includes tools like word processors, spreadsheets, and project management apps. These tools enhance personal productivity.
What Is Enterprise Software Used For?
Enterprise software manages business processes on a large scale. It includes applications for customer relationship management, resource planning, and supply chain management. It optimizes business operations.
How Do Productivity And Enterprise Software Differ?
Productivity software is for individual efficiency. Enterprise software manages organizational processes. Productivity tools focus on personal tasks, while enterprise tools handle complex business operations.
Can Productivity Software Be Used In Enterprises?
Yes, productivity software can complement enterprise software. It helps employees manage daily tasks, improving overall efficiency within the organization. It supports enterprise goals.
Conclusion
Choosing the right software is crucial. Productivity software boosts individual tasks. Enterprise software supports large-scale business operations. Understanding your needs helps you decide. Smaller teams benefit from productivity tools. Large companies need enterprise solutions. Consider your goals and team size.
Make an informed choice. Your business will thrive with the right software.